A charge is a right created by any person including a company referred to as “the borrower” on its assets and properties, present and future, in favour of a financial institution or a bank, referred to as “the lender”, which has agreed to extend financial assistance.
| Table of Content |
Definition of Charge as per Companies Act & Transfer of Property Act
Definition of Charge as per Companies Act, 2013
Section 2(16) of the Companies Act, 2013 defines charges so as to mean an interest or lien created on the property or assets of a company or any of its undertakings or both as security and includes a mortgage.

Definition of Charge as per Transfer of Property Act, 1882
According to Section 100 where immovable property of one person is by act of parties or operation of law made security for the payment of money to another, and the transaction does not amount to a mortgage, it is called charge.
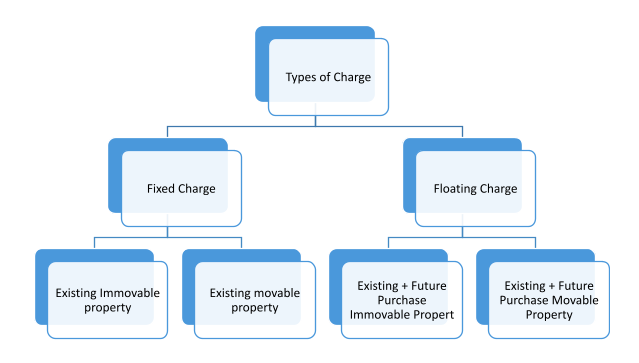
Types of Charges
Crystallization of Floating charge
(Conversion of Floating Charge in to Fixed Charge)
Meaning of Crystallization
‘Crystallization’ means that the right of the company to deal in the assets, which are subject of floating charge, comes to an end.
Cases in which crystallization takes place:
- Where the company is ordered to be wound up.
- Where the company ceases to carry on business.
- Where the company makes a default in payment of interest or repayment of principal to the charge holder in accordance with the terms of the charge, and the charge holder brings an action to enforce his security.
Registration of Charges
Section 77(1) provides that it shall be the duty of every company creating a charge
- Within or
- Outside India,
On its property or assets or any of its undertakings, whether tangible or otherwise, and situated in or outside India, to register the particulars of the charge signed by the company and the charge holder together with the instruments, if any, creating such charge in Form No. CHG-1 (for other than debentures) or Form No. CHG-9 (for debentures including rectification), with the Registrar within 30 days of its creation.
Provided that the Registrar may, on an application by the company, allow such registration to be made
(a) in case of charges created before the commencement of the Companies (Amendment) Ordinance, 2019, within a period of three hundred days of such creation; or
(b) in case of charges created on or after the commencement of the Companies (Amendment) Ordinance, 2019, within a period of sixty days of such creation, on payment of such additional fees as may be prescribed:
Provided further that if the registration is not made within the period specified
(a) in clause (a) to the first proviso, the registration of the charge shall be made within six months from the date of commencement of the Companies (Amendment) Ordinance, 2019, on payment of such additional fees as may be prescribed and different fees may be prescribed for different classes of companies;
(b) in clause (b) to the first proviso, the Registrar may, on an application, allow such registration to be made within a further period of sixty days after payment of such advalorem fees as may be prescribed.
Provided also that any subsequent registration of a charge shall not prejudice any right acquired in respect of any property before the charge is actually registered.
Provided also that this section shall not apply to such charges as may be prescribed in consultation with the Reserve Bank of India.
Certificate of Registration of Charge
Section 77(2) of the Act states that when a charge is registered with the Registrar under section 77(1), he shall issue a certificate of registration of such charge in Form No. CHG-2 and for registration of modification of charge in Form No. CHG-3, to the person in whose favour the charge is created.
(3) Notwithstanding anything contained in any other law for the time being in force, no charge created by a company shall be taken into account by the liquidator appointed under this act or the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016, as the case may be, or any other creditor unless it is duly registered and a certificate of registration of such charge is given by the Registrar.
(4) Nothing in sub-section (3) shall prejudice any contract or obligation for the repayment of the money secured by a charge.
Consequences of Non-Registration of charges
- Charge shall be void against the liquidator.
- Company shall be liable for the repayment of the money secured by the charge.
- The money secured by the charge shall be payable immediately.
- Company shall be punishable with fine minimum 1 lakh & max. 10 lakh.
- Officer in default liable to imprisonment up to 6 month or with a fine minimum 25000/- maximum 1 Lakh or with both.
Register of Charges
Register of charges shall be maintained by ROC and Company and every company shall keep at its registered office a Registrar of charges in Form CHG-7 and enter therein all particulars of charges registered with the Registrar any property, assets or undertakings of the company and the particulars of any property acquired subject to a charge as well as particulars of any modification of a charge and satisfaction of charge.


