
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) has transformed the tax regime in India, introducing a unified tax structure that optimize the way of business operate. One essential aspect of GST compliance is the generation of GST invoice- Invoicing under GST, which play a crucial role in documenting and facilitating the movement of goods and services. Understanding the fundamentals of a GST invoice- Invoicing under GST and the invoicing process is essential for businesses to comply with GST regulations and ensure smooth operations. In this article, we will provide a simple introduction to GST invoices- Invoicing under GST and delve into the key aspects of invoicing under the GST system.
What do you mean by e-invoice/ GST Invoice- Invoicing under GST?
E-invoicing under GST system refer to digitally generated invoices that are created, validated, and registered on the government’s Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) (GST e-invoice portal). GST e-invoice is a system implemented by the Indian government to standardize and streamline the invoicing process.
When a business generates an e-invoice, it undergoes a standardized format and digital validation process. The invoice data is uploaded to the IRP, which validates the invoice and assigns a unique Invoice Reference Number (IRN) to each e-invoice. The IRP also adds a digital signature and a Quick Response (QR) code to the invoice.
The e-invoice in GST format contains all the necessary details required for a valid GST invoice, such as supplier details, recipient details, invoice line items, tax amounts, and other relevant information. The e-invoice is then digitally signed by the supplier using a digital signature certificate (DSC).
The purpose of implementing e-invoices in GST is to bring uniformity, transparency, and efficiency to the invoicing process. E-invoicing under GST aims to reduce errors, promote compliance, facilitate data reconciliation, and enable seamless integration of invoice data with the GST system.
Information required in a GST Invoice- Invoicing under GST
A GST invoice in India should include the following information:
- Invoice Header:
- Name, address, and GST Identification Number (GSTIN) of the supplier.
- Invoice number (unique identification number for the invoice).
- Date of issuance.
- Supplier’s and Recipient’s Details:
- Name, address, and GSTIN of the recipient (if registered under GST).
- If the recipient is unregistered, their name and address along with the words “Unregistered Person” should be mentioned.
- Invoice Line Items:
- Description of the goods or services supplied.
- Quantity or volume of the goods or services.
- Unit of measurement.
- Rate per unit.
- Taxable value (total value of goods or services before applying GST).
- Applicable GST Rates:
- The GST rate for each item (e.g., CGST, SGST/UTGST, IGST).
- HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) code or SAC (Service Accounting Code) for the goods or services supplied.
- Taxes and Discounts:
- Amount of CGST (Central Goods and Services Tax).
- Amount of SGST (State Goods and Services Tax) or Union Territory Goods and Services Tax (UTGST).
- Amount of IGST (Integrated Goods and Services Tax) for interstate transactions.
- Any applicable cess.
- Discounts offered (if applicable).
- Total Invoice Amount:
- Total taxable value.
- Total GST amount.
- Total (including taxable value and GST).
- Payment Details: Payment terms, if applicable (e.g., due date, payment method).
- Other Information:
- Place of supply (state/union territory where the supply is made).
- Shipping address (if different from the recipient’s address).
- The signature or digital signature of the supplier or authorized representative.
Who must generate invoicing under GST and its applicability?
E-invoicing applies to certain businesses in India based on their turnover thresholds. Here are the following entities are required to generate invoicing:
- Businesses with Annual Aggregate Turnover (AATO) exceeding INR 500 crore: Entities with a turnover exceeding INR 500 crore in any financial year from 2017-18 onwards are mandated to generate e-invoices for all B2B (business-to-business) transactions.
- Businesses with AATO between INR 100 crore and INR 500 crore: From January 1, 2022, businesses with an annual aggregate turnover between INR 100 crore and INR 500 crore are required to generate e-invoices for B2B transactions.
- Businesses with AATO INR 50 crore: From April 1, 2021, businesses with more than INR 50 crore are required to generate invoicing under GST for B2B transactions.
- Businesses with AATO INR 20 crore: From April 1, 2022, businesses with more than INR 20 crore are required to generate invoicing under GST for B2B transactions.
- Businesses with AATO INR 10 crore: From October 1, 2022, businesses with more than INR 10 crore are required to generate invoicing under GST for B2B transactions.
- Businesses with AATO INR 5 crore: From August 1, 2023, businesses with more than INR 5 crore are required to generate invoicing under GST for B2B transactions.
Process of getting an Invoicing under GST
To generate an e-invoice in India, businesses need to follow a specific process. Here is a general outline of the steps involved:
- Implementing the necessary technical infrastructure: Businesses must ensure they have the required technical capabilities to generate e-invoices. This typically involves integrating their invoicing or accounting software with the government’s IRP or using third-party solutions that facilitate e-invoicing.
- Preparing the invoice details: Businesses need to compile all the necessary information required for the e-invoice, including supplier details, recipient details, invoice line items, tax details, and other relevant information.
- Generating the e-invoice: Using integrated software or third-party solutions, businesses generate the e-invoice by inputting the invoice details. The software may have built-in validation checks to ensure compliance with e-invoicing rules.
- Registering the e-invoice on the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP): The generated e-invoice is sent to the government’s IRP (GST portal e-invoice) or registration. The IRP validates the invoice details and assigns a unique IRN to the e-invoice. It also adds a digital signature and a QR code to the invoice.
- Signing and sharing the e-invoice: After the e-invoice is registered and the IRN is obtained, the invoice is digitally signed by the supplier using a DSC. The signed e-invoice, along with the QR code, is then shared with the recipient through electronic means, such as email.
- Updating the accounting records: Once the e-invoice is generated and shared, businesses need to update their accounting records to reflect the e-invoice details accurately. This ensures consistency between the e-invoice and their internal financial records.
Time limit to generate invoicing under GST
Starting from May 1, 2023, there is a specific time limit imposed on taxpayers with an AATO equal to or exceeding INR 100 crore for generating e-invoices. According to the new requirement, e-invoices for tax invoice under GST and credit-debit notes must be generated within 7 days of the invoice date.
Furthermore, for taxpayers other than those with an AATO equal to or exceeding INR 100 crore, there is no defined time limit or period within which e-invoices must be generated. However, these taxpayers should generate e-invoices on or after the invoice/CDN date, preferably around a week before filing their GSTR-1 returns.
On May 6, 2023, the GST department decided to extend the deadline for reporting old e-invoices on the IRP portals by three months. The original time limit of 7 days for reporting has been deferred. However, as of now, the department has not announced the new implementation date for this revised deadline.
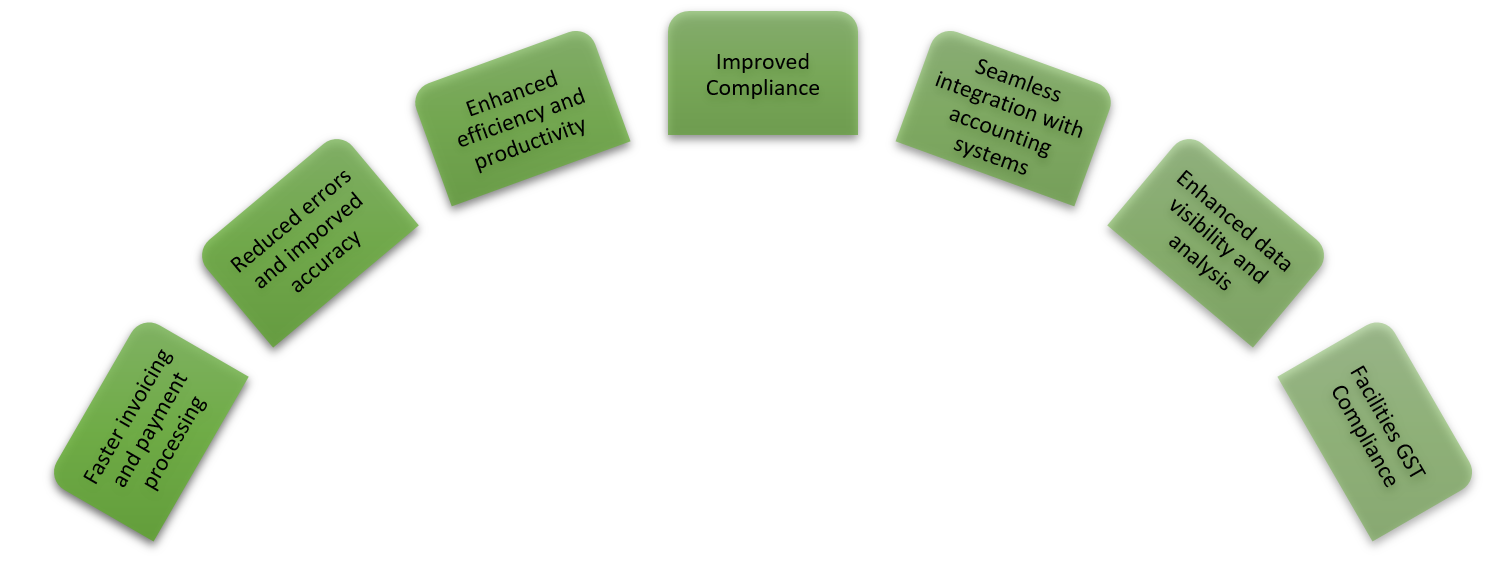
Benefits of Invoicing under GST
E-invoicing offers several benefits to businesses. Here are some key advantages:
Takeaway
Invoicing under the GST system is a critical aspect of compliance for businesses in India. The implementation of GST has standardized the invoicing process and introduced the concept of e-invoices, bringing efficiency and transparency to business transactions. By understanding the requirements and best practices of GST invoicing, businesses can streamline their operations, maintain accurate records, and avoid penalties or audits. Leveraging technology solutions for e-invoicing can further optimize the invoicing process, saving time and resources.







